Build a Pipeline with Azure Data Factory
Building a pipeline with Azure Data Factory.
ETL process
- Collect data sources
- Clean/join them with Dataflow and PowerQuery
- Create a master dataset
- Move the dataset to SQL Server
Data Sources
Underrepresented and minority-owned companies found through Data.gov and the DOT website, also known as DBE or Disadvantaged Business Enteprise. There is a DBE website for every US state.
The US Department of Transportation has a website with all US states and their corresponding DBE websites here. However, most of those links didn’t work.
Using the google query unified certification program, leads you to most states DBE websites. Many of them use the same platform that lets you export the data.
This is a sample of one of the files with a sea of rows:
Create an Azure Data factory
Follow my tutorial Create an Azure Data Factory
Review the CSV files to build a schema
I did an initial processing of the data exports. They were in Excel and CSV with a lot of extra header/footer rows. A few didn’t export correctly, and decided not to include them, as it would take me hours trying to clean them.
Many of them had these columns, while others had different column names, and more or fewer columns.
"Company Name","DBA Name","Owner First","Owner Last","Physical Address","City","State","Zip","Mailing Address","City","State","Zip","Phone","Fax","Email","Website","Agency","Certification Type","Capability","County","Work Districts/Regions","SBE Certification"
Schema columns
I decided to use these columns. The insights could be to find the number of DBE companies by city or state. Or place them on a US map dashboard.
CompanyName, DBAName, Address, City, State, Zip, Website, Agency, CertificationType, Capability, County
Upload the data to the storage container
I created a container named dbeapp with two directories:
inputCSV: I uploaded12CSV filesoutputJoinedCSV: I will use this after joining all files.
Follow my tutorial Create an Azure Blob Storage and Container
Connect to the SQL Server Database
See Create an Azure SQL Database.
After the SQL Server and Database were created.
- Go to the database
- Query editor
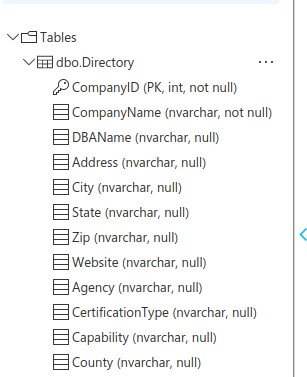
Create a table to hold the data:
CREATE TABLE Directory (
CompanyID int PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
CompanyName nvarchar(100) NOT NULL,
DBAName nvarchar(100),
Address nvarchar(100),
City nvarchar(50),
State nvarchar(20),
Zip nvarchar(10),
Website nvarchar(50),
Agency nvarchar(20),
CertificationType nvarchar(20),
Capability nvarchar(100),
County nvarchar(50)
)
However, much later in the process, I had problems with the data pipeline, and had to change the column lengths. More about this later.
In another blog post, I am going to build a star schema from this database since:
Directoryis not the best name for this table, change toCompany- Extract address information into a
CompanyAddresstable (since a company can have many address values) - I think
AgencyandCertificationTypemight have a few dozen unique values and they can be in separate tables - The database can have a fact table to make PowerBI easier to query than creating DAX calculations
Open the Tables to verify that the query ran correctly. I can see the columns in dbo.Directory
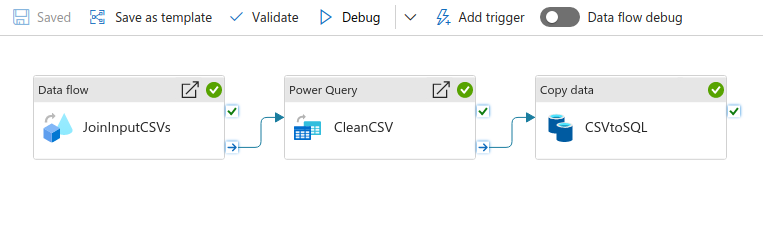
Data Factory Components
We have to process the CSV files before combining them, since some files have different column names and number of columns.
Create a Pipeline
- Create a Pipeline for the project
Create Linked Services
These connect ADF to different services:
- For the Blob container
- For SQL Server
Create Datasets
A dataset is a view that points to the data at a service.
- 1 to join the output of the Data Flow
- 1 for PowerQuery output
- 1 for SQL Server
Create a Data Flow
- Create a Data Flow to process each CSV file
Create a Copy Activity
- A Copy Activity from PowerQuery output to SQL Server
There is a Youtube tutorial about some of the above workflow here
Create a Pipeline in Data Factory
- On the left menu, go to the Author/Edit interface.
- Under
Pipeline, selectNew Pipeline - Name:
Blob CSV to SQL Save allto commit to the repository
Create Linked Services
Follow my tutorial to create an Azure Data Factory Linked Service
- For the Blob container. I named it
InputBlob - For SQL Server. I named it
OutputSQL
Create Datasets
Create a Dataset to join the output of the Data Flow
We need to transform the CSV files from the Azure Blob, clean the data, and join them to a dataset. The input files are in the container (and directory) dbeapp/inputCSV/. The output container is dbeapp/outputJoinedCSV/.
See Azure Data Factory Dataset
- Type:
Azure Blob Storage - Name the dataset
OutputDataflowCSV - Linked service
InputBlob - File path
dbeapp/outputJoinedCSV/dbe-joined.csv
Using an input Dataset for PowerQuery processing
We will use this file dbeapp/outputJoinedCSV/dbe-joined.csv as the input dataset for PowerQuery.
Create a dataset for the PowerQuery result
See Azure Data Factory Dataset
- Type:
Azure Blob Storage - Name the dataset
OutputPowerQueryCSV - Linked service
InputBlob - File path
dbeapp/outputJoinedCSV/outputPowerQuery.csv
Create a Dataset for the output SQL Server
See Azure Data Factory Dataset
- Type:
Azure SQL Database - Name the dataset
OutputSQLTable - Linked service
OutputSQL - In
Table, select the table that was created above, in my casedbo.Directory
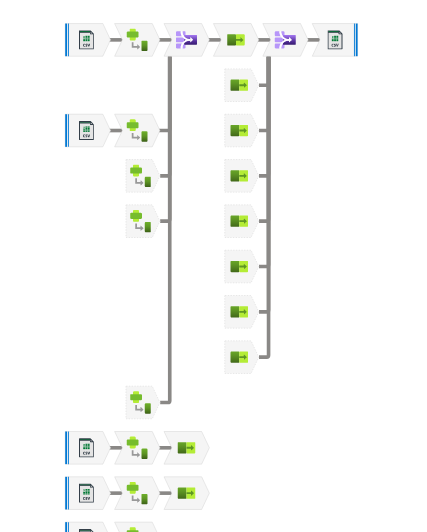
Create a Data Flow to process each CSV file
There are two transformation features in Azure Data Factory. Which one to use depends on the data source.
- Power Query: It requires a dataset in Data Factory
- Data Flow: It can use a dataset in Data Factory or a CSV file from Azure Blob
Since all the files are CSVs in the Azure Blob container. We are using Data Flow.
Follow my post Azure Data Factory Data Flow for a detailed tutorial on this process.
Final result of the Data Flow, zoomed in:
Create a PowerQuery resource
Modify the dataset with PowerQuery
When creating the table in SQL Server, I assumed a limit of characters for each column. For example:
State nvarchar(20),
Zip nvarchar(10),
Capability nvarchar(100),
- I assumed that
Statecould have been entered with two characters or with the full name. - With
Zipmaybe it was entered with 5 digits or with 9 digits plus the dash character. - For
Capabilityduring initial data exploration, this was a description of the company, and the few rows I saw weren’t that long.
Why use PowerQuery now?
Later when you execute the Copy Activity to SQL Server. It might not work and throw an error that the data is being truncated.
- We could modify the dataset to match the data type lengths and/or
- Clean the dataset and modify the data type lengths in SQL Server
Create a PowerQuery resource
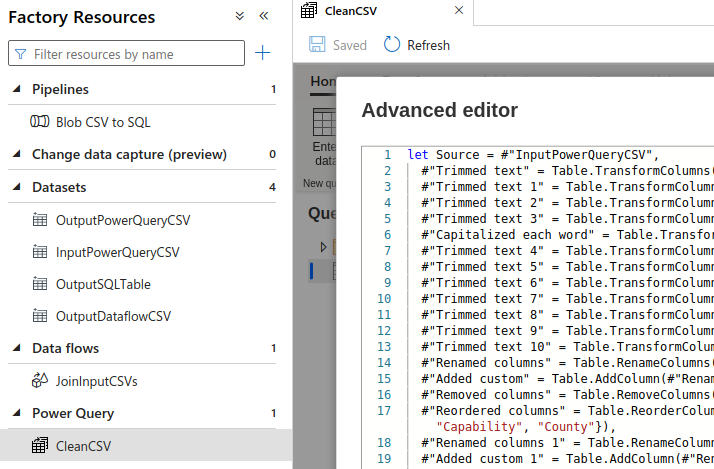
- In Data Factory, Author interface, Factory Resources
- Go to Power Query, create
New power query - Rename it, for example
CleanCSV - Select a dataset,
OutputDataflowCSV - PowerQuery opens as an iframe
Save allto commit to the repository
Process the data with PowerQuery
- Many columns had white space. I transformed all the columns to
Trimthem - Another column had too many characters and I decided to truncate it to
250characters- Formula
Text.Start([Capability], 250)
- Formula
- I also removed duplicates by
CompanyName + Address + CertificationType- There were repeated rows but had different
CertificationType
- There were repeated rows but had different
Save allto commit to the repository
Correct the Table in SQL Server
Go to the SQL Server Table, then Query Editor. Recreated the table to map the max lengths for each column.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS [dbo].[Directory];
GO
CREATE TABLE Directory (
CompanyID int PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
CompanyName nvarchar(100) NOT NULL,
DBAName nvarchar(150),
[Address] nvarchar(150),
City nvarchar(50),
[State] nvarchar(2),
Zip nvarchar(5),
Website nvarchar(150),
Agency nvarchar(20),
CertificationType nvarchar(20),
Capability nvarchar(260),
County nvarchar(50)
);
GO
Add PowerQuery to the Pipeline
- In Data Factory, Author interface, click on the Pipeline
- In Activities/Power Query, drag/drop
Power Queryto the graph canvas- Add a name, I entered
CleanCSV Settingstab- Select the PowerQuery created previously
- Run on Azure or IR, leave default
AutoResolveIntegrationRuntime - Compute type, leave default
General purpose - Core count, leave default
4 (+4 Driver cores)
Sinktab- Select as
Sinkthe dataset created aboveOutputPowerQueryCSV - On the same row, click on the
Settingsicon Settingstab, file name optionOutput to single fileand enter the file nameoutputPowerQuery.csvOptimizetab, selectSingle partition
- Select as
- Add a name, I entered
Connect Data flow to Power Query
- Click on the
Data Flowcomponent - On the small right-arrow, drag/drop this arrow to the Power Query component
- This means on Data Flow completion, do the next step Power Query.
Save allto commit to the repository
Errors with PowerQuery
- If PowerQuery shows that
Cannot connect to one of the data sources - Make a backup of the steps you did so far, by going to the last step
- Click on
Advanced Editorand copy/paste the code somewhere safe - Delete the PowerQuery resource
- Add it again
- Reload the steps
Create a Copy Activity from PowerQuery output to SQL Server
- Go to the Author/Edit interface
- Go to the Pipeline
- Under
Move & Transform - Drag/drop
Copy datato the canvas (on the right) - Name:
CSVtoSQL - Go to the
Sourcetab and select theSource dataset. Select theOutputPowerQueryCSVdataset - Go to the
Sinktab and select theSink dataset. Select theOutputSQLTabledataset- In
Pre-copy scriptenterdelete from your-table-name- For example
delete from Directory(my table was calledDirectory) - This is similar to saying
IF EXISTS(something)...DELETE FROM your-table-name
- For example
- In
- Go to the
Mappingtab to verify the input columns map correctly to the output ones.- Click on
Import schemas
- Click on
Save allto commit to the repository
Connect the Power Query activity to the Copy Data
- Click on the Power Query activity
- On the small right-arrow, drag/drop this arrow to the Copy Data component
- This means on Power Query completion, do the next step Copy Data.
Save allto commit to the repository
Error: Copy activity CSVtoSQL
I initially didn’t add PowerQuery to clean the data and got this error:
Failure happened on 'Sink' side. ErrorCode=SqlOperationFailed,'Type=Microsoft.DataTransfer.Common.Shared.HybridDeliveryException,Message=A database operation failed. Please search error to get more details.,Source=Microsoft.DataTransfer.ClientLibrary,''Type=System.InvalidOperationException,Message=The given value of type String from the data source cannot be converted to type nvarchar of the specified target column.,Source=System.Data,''Type=System.InvalidOperationException,Message=String or binary data would be truncated.,Source=System.Data,'
The error means that the output will truncate the input because the data types don’t match. I found out that the lengths I defined in the output were too short. I added a PowerQuery activity as described previously.
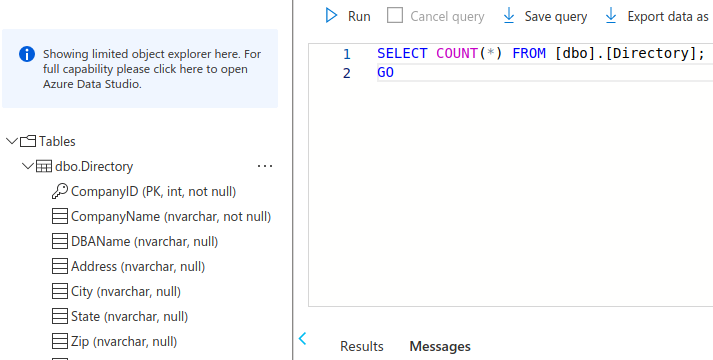
Verify the data copied from Input Blob To SQL Server
- Go to SQL Server database
- Query editor
- Run a query
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM your-database-name - Verify the results
Run again using a Trigger
So far the pipeline ran in debugging mode. Create a trigger to keep a record of a run in the Monitor interface.
- Go to the Data Factory
Add trigger, thenTrigger Now.- It will monitor this run in the Monitor interface.
See more about triggers in Azure Data Factory Scheduling.
Publish
Click Publish to save everything into the adf_publish branch. An internal branch used by Azure Data Factory.
